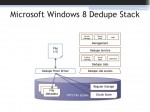
The next version of Microsoft Windows Server includes integrated data deduplication technology. Microsoft is positioning this as a boon for server virtualization and claims it has very little performance impact. But how exactly does Microsoft’s de-duplication technology work?
I/O
What is WRITE_SAME? Green Eggs and Ham!
One of the sticky wickets that holds back thin provisioning is the need to communicate when capacity is no longer needed. Enterprise storage arrays can reclaim zeroed pages, but writing all those zeros can really fill up an I/O queue. This is where WRITE_SAME comes into the picture.
Zero Page Reclaim: Savior of Thin Provisioning?
On the storage side, arrays can only use the information they have to deallocate: The data that’s stored on them. They don’t know what application is using it, what file system it is. But, somewhere along the line, someone had a big idea and said, “wait a second, what if we look for pages that are all zeros?” We’ll talk about pages a bit later, but for now, let’s talk about zeros. A zero is kind of a smoke signal coming up from over the hills that says, “there’s nothing valuable here.”
Innocence, Fairness, and Technology Benchmarks
HP recently commissioned Tolly Group to benchmark their BladeSystem c7000 against the Cisco UCS 5100. The short report focuses on two results, and reads like so many competitive benchmarks in the IT industry: Tolly focuses on metrics that highlight the strength of HP’s solution and the weaknesses of Cisco’s. What’s the real value of pinpoint maximum-performance benchmarks like this?